In today’s digital-first world, if your business isn’t showing up online, it’s practically invisible.
That’s where SEO—Search Engine Optimization—steps in as a game-changer. SEO helps websites climb search engine rankings, get discovered, and convert casual visitors into loyal customers.
This guide will cover each key aspect of SEO and point you toward valuable resources for further learning.
What Is SEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the practice of optimizing your website to improve its visibility when people search for products or services related to your business on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
The ultimate goal? To rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), bring in organic traffic, and deliver value to your users.
Imagine you’re a bakery owner. When someone searches for “best chocolate cake near me” on Google, SEO is what helps decide whether your bakery appears on the first page—or gets lost way back on page seven.
How is SEO different from SEM and PPC?
SEM and PPC are also commonly referenced in discussions related to SEO. To really understand SEO, it helps to know what it is—and what it isn’t.
In this guide, we’ll break down these terms, explain what each abbreviation means, and show how they relate to different areas of digital marketing.
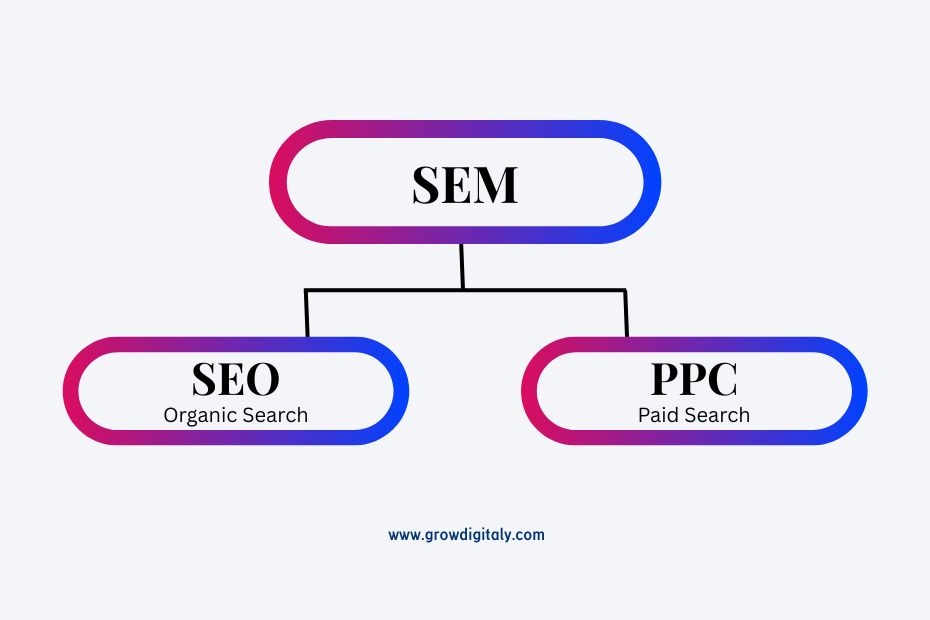
SEO vs. SEM
SEM stands for Search Engine Marketing. It is also known as search marketing. It’s a type of digital marketing focused on getting traffic from search engines like Google. SEM is a broad term that includes both SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and PPC (Pay-Per-Click advertising, such as Google Ads).
So, how are SEO and SEM different?
Technically, they’re not completely separate—SEO is actually a part of SEM.
- SEO: Brings in free (organic) traffic from search engines
- PPC: Brings in paid traffic through ads
- SEM: Covers both organic and paid methods
A simple way to picture it:
Think of SEM as a coin.
- SEO is one side (organic traffic)
- PPC is the other side (paid traffic)
Both sides work together to bring people to your site through search engines.
SEO vs. PPC
PPC stands for Pay-Per-Click – it’s a form of digital marketing where advertisers pay each time someone clicks on their ad.
Here’s how it works:
Advertisers choose keywords or phrases they want their ads to show up for in search engine results. When someone searches for those terms, the ad appears near the top of the page as a paid listing. If the user clicks, the advertiser pays.
Back to our coin analogy:
If Search Marketing is a coin, then SEO and PPC are its two sides.
- With PPC, you pay for each click on your ad.
- With SEO, your listing appears in the results without paying per click, but it still requires time, effort, and investment to rank organically—so it’s not truly “free.”
People often compare SEO and PPC to see which delivers a better return on investment (ROI). But the truth is, they’re most effective when used together.
In the marketing world, the terms SEM and PPC are sometimes used interchangeably. But here, when we say SEM, we mean both SEO (organic search) and PPC (paid search).
Why SEO Matters (A Lot More Than You Think)
1. Visibility and Rankings
The higher your website ranks on search engines, the more people will see it. And let’s be honest—most users don’t go past the first page of search results.
2. Organic Traffic = Real People
SEO brings in organic traffic, which means visitors who find you naturally through search—not because you paid for ads.
3. Trust and Credibility
Users trust Google. If you rank well, that trust rubs off on your brand.
4. Better User Experience
A key part of SEO is improving the usability and speed of your website, which makes your visitors happy (and more likely to convert).
5. High ROI
Compared to paid ads or social media marketing, SEO delivers one of the best long-term returns on investment.
SEO is important because search engine results pages (SERPs) have many ads and special boxes, so you need SEO to get noticed. These SERP features include:
- AI Overviews.
- Featured snippets.
- Knowledge panels.
- Maps.
- Paid Ads (Sponsored Ads)
- Images.
- News – Top stories
- Videos.
- Short Videos
- Forum
- People Also Ask.
- Carousels.
The 3 Pillars of SEO (Types of SEO)
SEO isn’t one single technique—it’s an ecosystem of strategies that work together to push your website up the ranks. Let’s break it down.

1. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO includes everything you can change on your own website.
A. Keywords
Start by figuring out what your audience is searching for. These are your keywords.
You can use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or Moz Keyword Explorer.
Focus on long-tail keywords like “how to bake gluten-free bread” instead of broad terms like “bread.”
B. Title Tags
Every page should have a unique, descriptive title tag that includes your keyword.
✅ Example:
- Bad: Home
- Good: Buy Affordable Running Shoes – Free Shipping
C. Meta Descriptions
This short summary appears below your title in search results. Make it enticing and keyword-rich.
D. Header Tags (H1-H6)
Use headers to structure your content. Your main headline should be wrapped in <h1>, subtopics in <h2>, and so on.
E. Image Alt Text
Google can’t “see” images, so use alt text to describe them. This boosts SEO and accessibility.
F. Content Quality
Google LOVES fresh, high-quality, and original content.
- Answer your users’ questions.
- Use bullet points, numbered lists, and short paragraphs.
- Include internal and external links.
2. Technical SEO
If on-page SEO is about what’s on your site, technical SEO is about how your site works behind the scenes.
A. Site Speed
Slow websites kill rankings. Compress images, use caching, and minimize JavaScript.
B. Mobile-Friendliness
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it ranks the mobile version of your site first.
C. Secure Site (HTTPS)
SSL certificates are now a must. Users trust secure websites, and so does Google.
D. XML Sitemaps
This file helps Google understand your website structure and find your pages faster.
E. Robots.txt File
This tells search engines which parts of your site to crawl and which to skip.
F. Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Add rich snippets to your content—like ratings, FAQs, or product details—to stand out in search results.
3. Off-Page SEO
This includes everything you do outside your website to improve rankings.
A. Backlinks
Links from other websites to yours are SEO gold. But not all backlinks are created equal.
- High-quality backlinks from trusted sites (think Forbes, NY Times) matter the most.
- Focus on earning, not buying, links.
B. Social Signals
While not a direct ranking factor, social media helps amplify your content and attract backlinks.
C. Guest Blogging
Write for other blogs in your niche. Include a backlink to your site.
D. Reviews and Mentions
Encourage happy customers to leave reviews on platforms like Google My Business, Yelp, or Trustpilot.
Key Areas of SEO
SEO isn’t one-size-fits-all—there are several specialized branches within search engine optimization. Each comes with its own strategies, tools, and challenges that go beyond the basics of “regular” SEO.
Here are five common SEO specialties:
1. Ecommerce SEO
This focuses on online stores. It involves optimizing things like product pages, category pages, filters (faceted navigation), internal links, product images, reviews, and using structured data (schema) to help search engines understand your listings.
2. Enterprise SEO
This is SEO at a very large scale—usually for websites with millions of pages or huge organizations with complex structures and multiple teams. It often involves longer approval processes, working with development teams, and coordinating with many stakeholders.
3. International SEO
This is for businesses targeting multiple countries or languages. It includes optimizing multilingual or multiregional websites and making sure your content is visible on international search engines like Baidu (China) or Naver (Korea).
4. Local SEO
Local SEO helps businesses show up in search results for specific geographic areas. This includes optimizing for Google Maps, managing local listings, getting reviews, and making sure your business appears when people search for services “near me.”
5. News SEO
Speed is everything in news SEO. The goal is to get articles indexed and showing up in places like Google News, Google Discover, and Top Stories as fast as possible. It also involves using the right structured data, managing paywalls, and optimizing section pages.
How Search Engines Work (Simplified)
Ever wonder how Google decides which sites to show first?
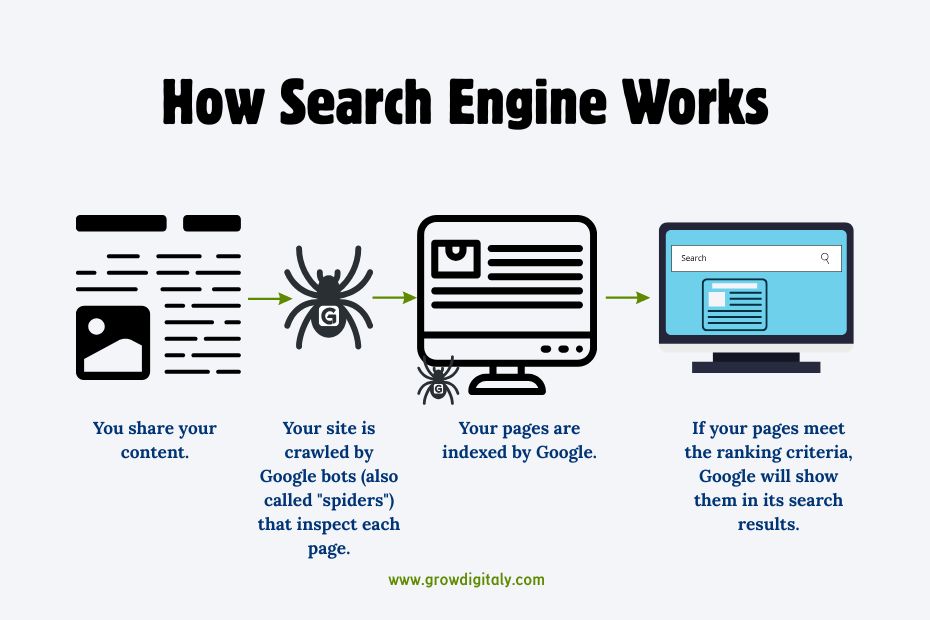
1. How Search Engines Actually Work
a. Crawling
Search engines use bots (called spiders) to crawl your website and collect information.
b. Rendering
Search engines use HTML, JavaScript, and CSS to determine how a web page will appear.
c. Indexing
The crawled data gets added to a massive library called an index.
d. Ranking
When someone searches(type any query) for something, search engines look at hundreds of factors to show the most relevant results.
2. Research: The Foundation of Effective SEO
Research is a crucial part of any successful SEO strategy. It helps guide your decisions, uncover opportunities, and align your efforts with your goals. Here are some key types of research that can boost your SEO performance:
Audience Research:
Understand who you’re trying to reach. Who are they (demographics and interests)? What problems are they facing? What questions are they asking that your content can answer?
Keyword Research:
Figure out which search terms people use to find your content. This helps you target valuable keywords with the right mix of demand and competition, and naturally incorporate them into your content.
Competitor Research:
Check out how your competitors are doing things. What kind of content are they creating? What keywords are they ranking for? What can you do better or differently?
Brand/Business/Client Research:
Know the business inside and out. What are its goals, and how can SEO help achieve them? Your strategy should support broader business objectives.
Website Research (SEO Audits):
SEO audits help identify problems and opportunities on your site. Focus on areas like technical SEO, content quality, backlinks, and signals of expertise, experience, authority, and trust (E-E-A-T).
SERP Analysis:
Look at what’s ranking on the search engine results page (SERP) for your main (target) keywords. What kind of content is ranking? What’s the search intent—are people looking to buy, learn, or find something? Use this insight to create content that aligns with what users (and Google) want.
3. Planning
An SEO strategy is your long-term action plan for improving visibility and driving traffic through search engines. It’s like a roadmap—your route may shift over time, but your destination (your goals) should stay clear and consistent.
To build a solid SEO plan, consider including:
- Setting clear goals, like OKRs or SMART goals
- Establishing timelines and milestones to set expectations
- Identifying the right KPIs and metrics to track success
- Deciding how work will be executed (in-house, agency, or hybrid)
- Aligning and communicating with stakeholders throughout the process
- Selecting and implementing tools to support your strategy
- Hiring and training the right team or defining team roles
- Setting and managing a budget for resources, tools, and people
- Measuring and reporting performance regularly
Documenting your strategy so everyone stays aligned and on track
Your SEO strategy isn’t static—it should grow and adapt with your business, your audience, and the search landscape.
4. Creating and Implementing
Once your research is complete, it’s time to take action and apply what you’ve learned. This usually involves:
Creating new content
Work with your content team to develop fresh, targeted content based on keyword and audience insights.
Improving existing pages
Update and enhance current pages by refining content, adding internal links, optimizing keywords and topics, or making other on-page improvements to boost performance.
Cleaning up outdated or low-quality content
Identify and remove pages that no longer serve a purpose—whether they’re not ranking, not bringing in valuable traffic, or not supporting your SEO goals.
5. Monitoring and Maintaining
Monitoring your website is essential—you need to know the moment something goes wrong.
Whether it’s a sudden drop in traffic to a key page, slow loading times, broken links, pages falling out of the index, or even your entire site going offline, staying on top of these issues helps you catch problems early and prevent bigger damage.
6. Analyzing, Assessing and Reporting on Performance
If you don’t measure your SEO efforts, you can’t improve them. To make smart, data-driven decisions, you’ll need to track performance using a few key tools:
A. Website analytics
Start with free essentials like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and Bing Webmaster Tools to monitor traffic, rankings, and technical issues.
B. SEO tools and platforms
You can choose from all-in-one SEO platforms or use specific tools for tasks like keyword tracking, site audits, or backlink analysis. If you have the resources and unique needs, you can even build custom tools.
Once you’ve gathered the data, it’s time to report on your progress. You can do this manually or with reporting software.
Good SEO reporting should:
- Be done regularly (monthly, quarterly, etc.)
- Compare current data to past periods (like year-over-year)
- Tell a clear story about performance, wins, and areas to improve
Tracking results helps you stay on course—and shows the real impact of your SEO work.
Ranking Factors That Matter Most (in 2025)
Search engines use over 200 factors to rank pages, but these are some of the most important.
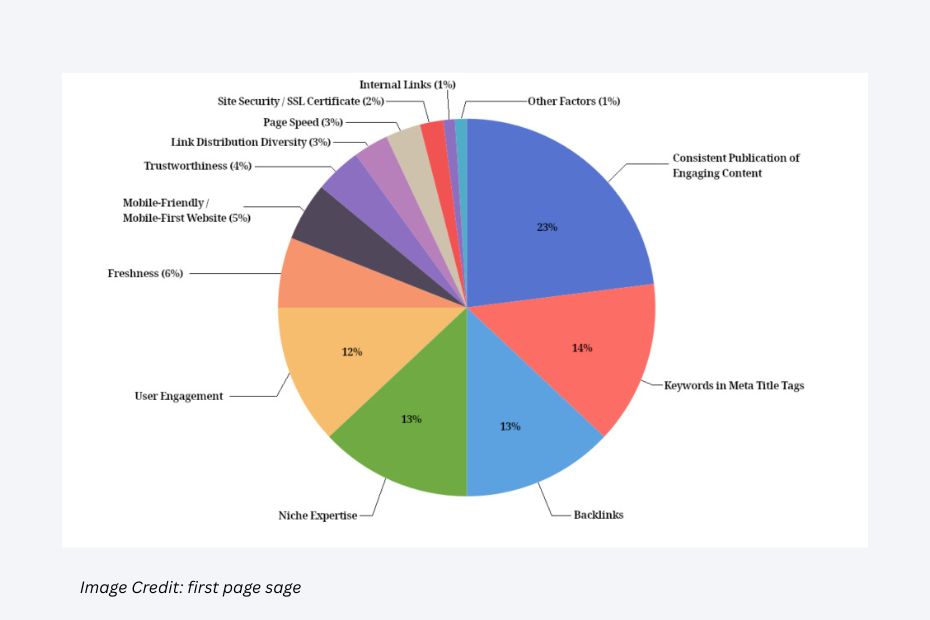
1. Page Speed
It is the time it takes for your website to load. Faster pages improve user experience and ranking.
Ideal: Under 3 seconds on desktop and mobile.
Google recommends aiming for under 2.5 seconds for mobile to provide a smooth experience.
2. Mobile Usability
This refers to how well your website works on mobile devices—easy to navigate, readable text, buttons sized for touch.
Ideal: Fully responsive design with no mobile usability errors detected in tools like Google Search Console.
3. Backlinks
Backlinks are links on other websites that lead people to your site. They signal authority and trust to search engines.
Ideal: High-quality, relevant backlinks from authoritative sites, rather than a large number of low-quality links.
4. Keyword Usage
Keywords are the search terms people use to find websites or answers. Using them strategically in your content helps your pages rank.
Ideal: Natural, relevant use of keywords in titles, headings, meta descriptions, and throughout content—avoid keyword stuffing.
5. Core Web Vitals
It is a set of metrics that show how good the user experience is. It includes:
- Loading speed (Largest Contentful Paint, LCP): Should be under 2.5 seconds
- Interactivity (First Input Delay, FID): Should be less than 100 milliseconds
- Visual stability (Cumulative Layout Shift, CLS): Should be less than 0.1
6. Content Freshness
Regularly updating or adding new content shows search engines your site is active and relevant.
Ideal: Update important pages periodically and publish fresh content regularly, depending on your niche.
7. User Engagement
Metrics like bounce rate (how quickly visitors leave) and time on site indicate how users interact with your site.
- Good bounce rate: Between 26% and 40%
- Average bounce rate: Between 41% and 55%
- Higher bounce rate: Between 56% and 70% — may need improvement
- Poor bounce rate: Above 70% — usually indicates issues with content, user experience, or relevance
Keep in mind:
- For blogs or single-page sites, a higher bounce rate is more common and might not be bad if users get the info they need quickly.
- For e-commerce or service sites, a lower bounce rate is usually better since you want visitors to explore more pages and take action.
So, aim to keep your bounce rate below 55%, but always consider the context of your site and audience.
Ideal: Low bounce rates and higher average time on site suggest valuable content and good user experience.
8. Secure and Accessible Website
Using HTTPS (secure connection) and ensuring your site can be crawled by search engines are crucial for SEO.
Ideal: Site fully secured with HTTPS and no accessibility issues detected by tools like Google Search Console.
By optimizing these areas to meet or exceed these benchmarks, you improve your site’s chances of ranking well and delivering a great user experience.
Content Is Still King (But Strategy Is Queen)
Creating content that ranks isn’t about stuffing keywords anymore. It’s about solving real problems.
Tips for SEO Content:
Start with keyword research
- Answer real user questions (check Google’s “People Also Ask”)
- Keep it easy to read: use headings, bullet points, and short sentences.
- Update old content regularly
- Use visuals (images, infographics, videos)
Local SEO: Dominate Your Neighborhood
If you run a local business, SEO can bring customers right to your doorstep.
How to Optimize for Local SEO:
- Set up and verify your Google Business Profile
- Use local keywords (“vegan bakery in Austin”)
- Get reviews on Google and Yelp
- Use NAP citations (Name, Address, Phone Number) consistently across directories
E-Commerce SEO: More Traffic, More Sales
If you run an online store, SEO can seriously boost your bottom line.
E-Commerce SEO Tips:
- Optimize product titles and descriptions
- Include schema markup for products
- Add user-generated content (reviews, Q&A)
- Improve site speed and mobile experience
Track, Measure, Improve
SEO isn’t set-it-and-forget-it. Monitor your performance and make updates when necessary.
SEO Tools to Use:
- Google Analytics: Track visitors, bounce rate, conversions
- Google Search Console: Check how Google indexes your site
- Moz/Ahrefs/SEMrush: Deep insights into rankings, backlinks, competitors
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Keyword stuffing
- Ignoring mobile optimization
- Duplicate content
- Buying low-quality backlinks
- Forgetting about meta descriptions
- Slow site speeds
- Poor site structure
SEO in 2025 and Beyond
SEO continues to evolve. Here’s what to keep an eye on:
- AI and Search (like Google’s SGE): AI will change how results are shown.
- Voice Search: People are asking questions like they talk.
- Video SEO: YouTube is the world’s #2 search engine.
- User Experience: Google’s algorithm is increasingly user-centric.
Final Thoughts
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the backbone of digital visibility. Whether you’re a solo blogger, a startup, or a massive e-commerce platform, the principles remain the same:
- Be discoverable
- Be helpful
- Be trustworthy
The journey may seem overwhelming at first, but remember: small, consistent improvements make all the difference.
If you want your website to thrive in search engines—and in the hearts of your visitors—SEO is where it starts.